参考资料:
https://blog.csdn.net/sikuon/article/details/75939434
https://blog.csdn.net/cassie_huang/article/details/62227023
https://blog.csdn.net/yeruby/article/details/41978199
最详细:https://blog.csdn.net/mj5742356/article/details/20125511
长短文件名 https://wenku.baidu.com/view/d729d62a680203d8cf2f2474.html
FAT16
一、关于需要掌握的基础知识
1.文件读写与文件指针的移动操作
2.十六进制计算
3.链表
4.小端序
二、FAT16文件系统的结构
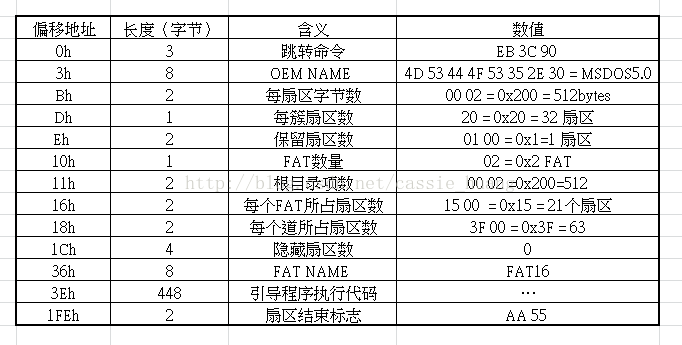
1.FAT16第一个扇区是DBR,是对整个分区的格式及参数进行说明的部分,从中可以读取到FAT所占扇区数、每簇扇区数、每个扇区的字节数、保留扇区数……
系统通过这些参数可以计算出FAT1、FAT2、根目录、数据区的位置,其中,保留扇区之后的即为FAT区,FAT区由两个完全相同的FAT1、FAT2构成,FAT2作为FAT1的一个备份,保障数据安全。
2.FAT1中存放了每个簇之间的对应关系以及自身的属性。
FAT2是FAT1的一个备份,以便于磁盘意外损坏的恢复
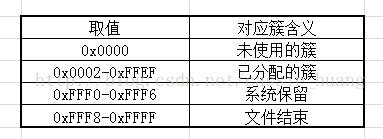
通过查表我们可以了解到这个簇到底是未被使用还是已被使用,以及这个簇后面还有没有链接到下一个簇。从而将连续的数据离散储存。
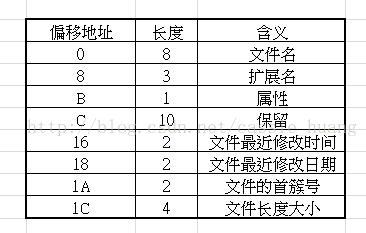
3.FAT2后的是根目录,根目录占用32个扇区,当中储存了根节点下面所拥有的所有文件和文件夹(文件夹可以当作一种特殊的文件),每个文件占用32个字节(当文件名过长的时候可能会占用更多空间),这32个字节分别对应的是这个文件对应的各种属性以及簇号。
我们可以通过寻找该簇来读取该文件的具体内容,如果是文件夹,这个簇中储存的是文件夹内的所有子目录元素(与根目录的作用类似)。
文件夹创建的时候会生成两个32字节的项
一个是 "." ,其中储存的是文件夹自身的信息
另一个是 "..", 储存了这个文件夹的父目录的信息(方便返回上一级)
三、删除文件(夹)的过程
找到描述该文件的那个32字节的项,将偏移值为0h的数据改为 E5,以说明该数据被删除。如果是文件夹的话,还应递归删除其目录下的所有文件。
四、创建文件(夹)的过程
在当前目录的簇下寻找一个空位置(32字节) 将新文件(夹)的信息写入,并且在磁盘中寻找一个未使用的新簇,将其分配给创建的文件(夹)
五、读取文件(夹)的过程
读取文件(夹)所对应的32字节数据,从而读取到整个文件的信息尤其是簇号,根据这个簇号去磁盘中的相应区域读取这个文件(夹)所储存的信息(文件)
六、写入文件的过程
类似于读取文件
七、遇到当前簇满的处理措施
在磁盘中寻找一个新簇,将原来的簇指向新簇,从而将两个簇连接在一起,形成一个连续的数据区域
八、注意事项
1.文件系统中的数据以小端序保存(数字的低位 存在 地址的低位上,这与普通人的思维有所区别)
e.g. 数据1234h, 用两个字节进行存储,则其在内存中的存储形式为: 34 12
2.DBR(DOS boot record) 占一个扇区,里面储存了整个文件系统的各种配置信息(如每个扇区的字节数,每个簇的扇区数,FAT区的个数,每个FAT所占扇区数等等)
3.FAT表中每个记录的位数成为FAT大小(fat16就代表一个簇的簇号所占空间为十六位,两个字节),这意味着一个fat16磁盘最多能储存20000h个簇,也就限制了fat16的一个分区的大小
八、相关图表
FAT16记录表(可先记录一下自己磁盘的如下信息,方便之后的分析,以下只是我自己SD卡的信息)
对于FAT16的一个分区:
每簇占多少个扇区:64
DBR(保留扇区数)0h
FAT1(FAT扇区数):标记某个簇的状态(已使用 未使用 坏簇),以两个字节为一个单位。 1000h
FAT2(FAT扇区数):与FAT1完全一样,作为FAT1的备份 1D800h
根目录(32个扇区) 3C000h
数据区(第二个簇) 40000h
第五个簇58000h
第六个簇60000h
DBR数据对照表
注意:1Ch: 20为文件 10为文件夹
文件信息对照表
系统时间与文件系统中的时间的换算
1.0x16~0x17中的时间=小时*2048+分钟*32+秒/2。
得出的结果换算成16进制填入即可。
也就是:
0x16字节的0~4位是以2秒为单位的量值;
0x16字节的5~7位和0x17字节的0~2位是分钟;
0x17字节的3~7位是小时。
2.0x18~0x19中的日期=(年份-1980)*512+月份*32+日。
得出的结果换算成16进制填入即可。
也就是:
0x18字节0~4位是日期数;
0x18字节5~7位和0x19字节0位是月份;
0x19字节的1~7位为年号,
原定义中0~119分别代表1980~2099,
目前高版本的Windows允许取0~127,即年号最大可以到2107年。
FAT16簇空间大小与分区空间大小的关系
| 表9 FAT16分区大小与对因簇大小 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 分区空间大小 | 每个簇的扇区 | 簇空间大小 |
| 0MB-32MB | 1 | 512个字节 |
| 33MB-64MB | 2 | 1k |
| 65MB-128MB | 4 | 2k |
| 129MB-225MB | 8 | 4k |
| 256MB-511MB | 16 | 8k |
| 512MB-1023MB | 32 | 16k |
| 1024MB-2047MB | 64 | 32k |
| 2048MB-4095MB | 128 | 64k |
文件操作函数:
fseek函数可以把位置指针调整到文件任意位置
fseek函数里需要提供一个基准位置和目标位置到基准位置间的距离,计算机根据他们计算出目标位置
SEEK_SET 0 把文件头作为基准位置
SEEK_CUR 1 把当前位置作为基准位置
SEEK_END 2 把文件尾作为基准位置
以下为完整代码:
程序结构设计有一点毛病,本来簇在读入程序之后可以切割成若干个32字节的块,方便操作。结果我把一个簇当成字符串处理了,所以写了很多个字符串操作函数
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define ISCMD(t) strcmp(a, t) == 0
#define COMMAND_MAX 100
#define SECTORS_PER_CLUST 1//每簇扇区数
#define BYTES_PER_SECTOR 512//每扇区字节数
#define SECTORS_PER_FAT 128//每FAT扇区数
#define RESERVED_SECTORS 1//保留扇区数
#define SECTORS_ROOT SECTORS_PER_CLUST//根目录的扇区数
#define CLUST_MAX_COUNT (SECTORS_PER_FAT * BYTES_PER_SECTOR >> 1) //簇的总个数
#define ROOT (RESERVED_SECTORS + SECTORS_PER_FAT * 2) * BYTES_PER_SECTOR//根目录的位置
#define CLUST_SECOND ROOT + SECTORS_ROOT * BYTES_PER_SECTOR//第二个簇的位置
FILE *fp;
struct clu{//一个簇
int status;
char byte[BYTES_PER_SECTOR * SECTORS_PER_CLUST + 10]; //簇里的扇区
}clust[CLUST_MAX_COUNT];
struct fi{//一个文件
bool dir;
char name[2][20];
int time;//修改时间
int date;//修改日期
int clust;//首簇号
long long len;//文件大小
fi *next;//下一个文件
}file[1 + CLUST_MAX_COUNT * SECTORS_PER_CLUST * BYTES_PER_SECTOR / 32];
int FileCnt, Clust_now;//当前文件的总个数与当前的簇
fi *HEAD;//头指针
char dir[10000][6];//存放所有文件夹名字的数组
int dir_now;
void Manu_Print();//打印帮助菜单
bool Command_Read();//读取命令
bool Data_ReadOrWrite(const int);//文件操作,读、写、关闭
void Data_Initialize();//初始化数据文件
void Data_Create_New();//创建新的类FAT16数据文件
void Data_Read();//将数据读入内存
void Data_Save();//保存文件
void Data_DBR_Print();//创建DBR
void Data_Add_A_File(fi *, int, int);//将clust中指定位置的字符串填充为新文件的信息
fi *Filelist_Search_File(char *, bool);//在已经读入的文件中寻找对应名称的文件
void Filelist_Update(int);//更新文件列表
void Filelist_Destroy();//文件列表清空
void Filelist_Add_File(fi *);//在文件列表中加入一个元素
void Filelist_Bubble_Sort();//用冒泡排序把文件列表按照字典序排序
void Filelist_Print();//打印出所有的文件
void File_Printf_Number(long long, int);//以小端序方式打印 (对文件)
long long File_Scanf_Number(int);//读取n个字节的小端序数字
void File_Printf_String(char *,int);//以字符串向文件输出信息
void File_Printf_32Bytes(fi *);//向文件中输出文件/文件夹的信息
void Str_Printf_Number(char *, long long, int);//以小端序方式打印 (对字符串)
long long Str_Scanf_Number(char *, int);//读取n个字节的小端序数字
void Str_Scanf_String(char *, int, char *);//以二进制格式读取字符串的内容
bool Str_Read_32Bytes(char *, fi *);//读取一个文件/文件夹的信息
void Str_Printf_32Bytes(char *, fi *);//向字符串中输出文件/文件夹的信息
void Str_Cut_Name_Into_Two(char *, char*, char*);//将一个文件名分隔为两部分
int Clust_Judge_Status(int); //判断该簇的状态
void Time_Print(int t);//输出时间
void Date_Print(int t);//输出日期
int Time_Get();//获取当前时间
int Date_Get();//获取当前日期
void Dir_Change(char *, bool);//更改目录位置
void Dir_Print();//打印当前目录
int Dir_Find_Empty(int);//在一个簇里面寻找空的位置
void Make_a_New_File(fi *, bool);//返回一个创建好的空文件
void Clust_Clear_File(int);//清理某个簇内的文件的所有信息
void Clust_Clear_Dir(int);//清理某个簇内的所有文件夹
int main(){
Data_Initialize();
Manu_Print();
bool FLAG = FALSE;
char rt[6] = "root:";
dir_now = 0;
strcpy(dir[dir_now], rt);
do{
Dir_Print();
printf(">");
FLAG = Command_Read();
}while(FLAG);
return 0;
}
bool Command_Read(){
char str[COMMAND_MAX], a[COMMAND_MAX], b[COMMAND_MAX];
gets(str);
sscanf(str, "%s%s", a, b);
if(str[0] == 0) return TRUE;
Filelist_Destroy();
Filelist_Update(Clust_now);
Filelist_Bubble_Sort();
if(ISCMD("ls") || ISCMD("dir")){
printf("\n\n");
Dir_Print();
printf(" contains the following files or directories:\n");
Filelist_Print();
}else if(ISCMD("cd")){
char temp[20];
strcpy(temp, b);
fi *t = Filelist_Search_File(temp, TRUE);
if(t != NULL && t->dir == TRUE){
Clust_now = t->clust;
if(strcmp(b, "..") == 0){
if(dir_now != 0)
Dir_Change(b, FALSE);//回退
}
else if(strcmp(b, ".") != 0)
Dir_Change(b, TRUE);
}else
printf("Invalid directory!\n\n");
}else if(ISCMD("mkdir")){
fi *t = Filelist_Search_File(b, TRUE);
if(t != NULL){//如果这个文件夹已经存在,就返回错误
printf("Directory already exists!\n");
return TRUE;
}else if(strlen(b) >= 8){
printf("Name too long!\n");
return TRUE;
}
int Clust_temp = Clust_now;
int k = Dir_Find_Empty(Clust_temp);
while(k == -1){
if(Clust_Judge_Status(clust[Clust_temp].status) == 0)
Clust_temp = clust[Clust_temp].status;//如果这个链表的其他簇还有空位
else{
int Clust_new = 2;//这个链表中已经不存在空位了,要找一个空簇,从第二个簇开始找
while(clust[Clust_new].status != 0) Clust_new++;
clust[Clust_temp].status = Clust_new;
clust[Clust_new].status = 0xFFFF;
Clust_temp = Clust_new;
}
k = Dir_Find_Empty(Clust_temp);//重新寻找空位
}
fi *F = (fi*) malloc(sizeof(fi));//填充基本信息
Make_a_New_File(F, TRUE);
clust[Clust_temp].status = 0xFFFF;
strcpy(F->name[0], b);//修改文件夹名称
Data_Add_A_File(F, Clust_temp, k);//把文件写入簇
fi *temp = (fi*) malloc(sizeof(fi));//再拿一个临时变量
Make_a_New_File(temp, TRUE);
char *p = clust[F->clust].byte;
strcpy(temp->name[0], ".");
temp->clust = F->clust; // .文件夹用于存放本文件夹的信息
Str_Printf_32Bytes(p, temp);
strcpy(temp->name[0], "..");
temp->clust = Clust_now; // ..文件夹用于存放上一个文件夹的信息
Str_Printf_32Bytes(p + 32, temp);
free(F);
free(temp);
}else if(ISCMD("create")){
//类似于新建文件夹,但是不用新建 .和..
fi *t = Filelist_Search_File(b, FALSE);
if(t != NULL){//如果这个文件夹已经存在,就返回错误
printf("Directory already exists!\n");
return TRUE;
}
char temp[20];//创建一个临时字符串
strcpy(temp, b);
Str_Cut_Name_Into_Two(temp, a, b);
if(strlen(a) >= 8 || strlen(b) >=3){
printf("Name too long!\n");
return TRUE;
}
int Clust_temp = Clust_now;
int k = Dir_Find_Empty(Clust_temp);
while(k == -1){
if(Clust_Judge_Status(clust[Clust_temp].status) == 0)
Clust_temp = clust[Clust_temp].status;//如果这个链表的其他簇还有空位
else{
int Clust_new = 2;//这个链表中已经不存在空位了,要找一个空簇,从第二个簇开始找
while(clust[Clust_new].status != 0) Clust_new++;
clust[Clust_temp].status = Clust_new;
clust[Clust_new].status = 0xFFFF;
Clust_temp = Clust_new;
}
k = Dir_Find_Empty(Clust_temp);//重新寻找空位
}
fi *F = (fi*) malloc(sizeof(fi));//填充基本信息
Make_a_New_File(F, FALSE);
clust[Clust_temp].status = 0xFFFF;
strcpy(F->name[0], a);//修改文件名称
strcpy(F->name[1], b);//修改文件后缀
Data_Add_A_File(F, Clust_temp, k);//把文件写入簇
}else if(ISCMD("rmdir")){
fi *t = Filelist_Search_File(b, TRUE);
if(t == NULL){
printf("no such a directory!\n");
return TRUE;
}
Clust_Clear_Dir(t->clust);
char temp[20];
strcpy(temp, b);
Str_Cut_Name_Into_Two(temp, a, b);//把文件名分割一下
char *st = clust[Clust_now].byte;
for(int i = 0; i < SECTORS_PER_CLUST * BYTES_PER_SECTOR / 32; i++){//寻找到簇中的那个文件,并且打上0xe5标记
fi *p = (fi*) malloc(sizeof(fi));
Str_Read_32Bytes(st + i * 32, p);
if(strcmp(p->name[0], a) == 0 && strcmp(p->name[1], b) == 0 && p->dir == TRUE){
*(st + i * 32) = 0xE5;
break;
}
}
/*
直接找到那个文件,首先递归删除该文件夹下的所有内容
然后再把本身 标记为删除
*/
}else if(ISCMD("rm")){
fi *t = Filelist_Search_File(b, FALSE);
if(t == NULL){
printf("no such a file!\n");
return TRUE;
}
Clust_Clear_File(t->clust);
char *st = clust[Clust_now].byte;
char temp[20];
strcpy(temp, b);
Str_Cut_Name_Into_Two(temp, a, b);
for(int i = 0; i < SECTORS_PER_CLUST * BYTES_PER_SECTOR / 32; i++){
fi *p = (fi*) malloc(sizeof(fi));
Str_Read_32Bytes(st + i * 32, p);
if(strcmp(p->name[0], a) == 0 && strcmp(p->name[1], b) == 0 && p->dir == FALSE){
*(st + i * 32) = 0xE5;
break;
}
}
//类似于删除文件夹,但不用递归删除
}else if(ISCMD("read")){
fi *t = Filelist_Search_File(b, FALSE);
if(t == NULL){
printf("no such a file!\n");
return TRUE;
}
int nxtClust = t->clust;
bool flag = 1;
printf("\nThis is what %s contains:", b);
printf("\n----------------------------\n");
while(flag == 1){
for(int i = 0; i < SECTORS_PER_CLUST * BYTES_PER_SECTOR; i++){
if(clust[nxtClust].byte[i] == 0){
flag = 0;
break;
}
printf("%c",clust[nxtClust].byte[i]);
}
if(Clust_Judge_Status(clust[nxtClust].status) == 1)
flag = 0;
else
nxtClust = clust[nxtClust].status;
}
printf("\n----------------------------\n\n");
/*
根据簇号直接搜索到对应的文件并且读入
*/
}else if(ISCMD("write")){
fi *t = Filelist_Search_File(b, FALSE);
if(t == NULL){
printf("no such a file!\n");
return TRUE;
}
int nxtClust = t->clust;
bool flag = 1;
char c;
while(flag == 1){
for(int i = 0; i < SECTORS_PER_CLUST * BYTES_PER_SECTOR; i++){
c = getchar();
if(c == -1){
flag = 0;
clust[nxtClust].byte[i] = 0;
break;
}else
clust[nxtClust].byte[i] = c;
}
clust[nxtClust].status = 0xFFFF;
if(flag == 0) break;
if(Clust_Judge_Status(clust[nxtClust].status) == 0)
nxtClust = clust[nxtClust].status;
else{
int tempClust = 2;
while(Clust_Judge_Status(clust[tempClust].status) != 2)
tempClust++;
clust[nxtClust].status = tempClust;
nxtClust = tempClust;
}
}
/*
边写文件边开新的簇
*/
}else if(ISCMD("format")){
printf("Are you sure to FORMAT this disk? (y/n): ");
gets(a);
if(ISCMD("y") || ISCMD("Y")){
printf("Once again. You'll lose your data, continue? (y/n): ");
gets(a);
if(ISCMD("y") || ISCMD("Y")){
printf("formating... ");
Data_ReadOrWrite(2);
Data_Create_New();
Data_ReadOrWrite(3);
Data_ReadOrWrite(1);
Data_Read();
Data_ReadOrWrite(3);
printf("done.\n\n");
}
}
}else if(ISCMD("save")){
printf("Are you sure to quit with saving? (y/n): ");
scanf("%s", a);
if(ISCMD("y") || ISCMD("Y")){
Data_Save();
return FALSE;
}
}else{
printf("unknown command \"%s\"\n",str);
}
return TRUE;//继续循环
}
bool Data_ReadOrWrite(const int t){//done
switch(t){
case 1: //只读
fp = fopen("fat16_data.bin", "rb");
return fp != NULL;
case 2: //可写
fp = fopen("fat16_data.bin", "wb");
return fp != NULL;
case 3:
fclose(fp);
return 1;
}
}
void Data_Initialize(){//done
if(Data_ReadOrWrite(1) == FALSE){
printf("Disk data doesn't exist. \nCreating a new one...\n");
Data_Create_New();
}
Data_ReadOrWrite(3);//关闭文件
Data_ReadOrWrite(1);//只读模式
Data_Read();
printf("Data loaded successfully.\n\n");
Clust_now = 1;
Data_ReadOrWrite(3);
}
void Data_Read(){
fseek(fp, BYTES_PER_SECTOR, SEEK_CUR);//跳过DBR区域
for(int i = 0; i <= -1 + SECTORS_PER_FAT * BYTES_PER_SECTOR >> 1; i++)//注意,这里是从0开始读
clust[i].status = (int) File_Scanf_Number(2);//读取FAT1
fseek(fp, SECTORS_PER_FAT * BYTES_PER_SECTOR, SEEK_CUR);//跳过FAT2
fread(clust[1].byte, sizeof(char), BYTES_PER_SECTOR * SECTORS_ROOT, fp);//读取根目录
for(int i = 2; i <= CLUST_MAX_COUNT; i++)
fread(clust[i].byte, sizeof(char), BYTES_PER_SECTOR * SECTORS_PER_CLUST, fp);//读取数据区
}
void Data_Create_New(){//done
Data_ReadOrWrite(2);
Data_DBR_Print();
for(int k = 0; k <= 1; k++){//填充FAT区域
fprintf(fp, "%c", 0xFF);
fprintf(fp, "%c", 0xFF);
for(int i = 1; i <= SECTORS_PER_FAT * BYTES_PER_SECTOR - 2; i++)
fprintf(fp, "%c", 0);
}
fi *p = (fi*) malloc(sizeof(fi));
Make_a_New_File(p, TRUE);
strcpy(p->name[0], ".");
File_Printf_32Bytes(p);
strcpy(p->name[0], "..");
File_Printf_32Bytes(p);
free(p);
for(int i = 2; i < (SECTORS_PER_CLUST * CLUST_MAX_COUNT) * BYTES_PER_SECTOR; i++)
fprintf(fp, "%c", 0);//把空扇区刷为0
Data_ReadOrWrite(3);
}
void Data_Save(){
Data_ReadOrWrite(2);
Data_DBR_Print();
for(int j = 0; j <= 1; j++)
for(int i = 0; i <= -1 + SECTORS_PER_FAT * BYTES_PER_SECTOR >> 1; i++)
File_Printf_Number(clust[i].status, 2);//打印FAT表,打印两份
fwrite(clust[1].byte, sizeof(char), BYTES_PER_SECTOR * SECTORS_ROOT, fp);//保存根目录
for(int i = 2; i <= CLUST_MAX_COUNT; i++)
fwrite(clust[i].byte, sizeof(char), BYTES_PER_SECTOR * SECTORS_PER_CLUST, fp);//保存数据区
Data_ReadOrWrite(3);
}
fi *Filelist_Search_File(char *name, bool IsDir){
char a[20], b[20];
Str_Cut_Name_Into_Two(name, a, b);
for(fi *p = HEAD; p != NULL; p = p->next)
if(strcmp(a, p->name[0]) == 0 && strcmp(b, p->name[1]) == 0 && p->dir == IsDir)
return p;//找到了
return NULL;//没找到
}
void Filelist_Print(){
printf("\n\n");
for(fi *p = HEAD; p != NULL; p = p->next){
Date_Print(p->date);
printf(" ");
Time_Print(p->time);
printf(" ");
printf("%s\t\t", p->dir == TRUE?" ":"");
printf("%s",p->name[0]);
if(!p->dir && p->name[1][0] != 0) printf(".%s", p->name[1]);
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n\n");
}
void Filelist_Update(int id){
if(id <= 0) return;
fi t;
for(int i = 0; i < SECTORS_PER_CLUST * BYTES_PER_SECTOR / 32; i++)
if(Str_Read_32Bytes(clust[id].byte + 32 * i, &t)){//如果读取成功,就申请一段新内存来存文件
fi *p = (fi *) malloc(sizeof(fi));
*p = t;
p->next = NULL;
Filelist_Add_File(p);
}
if(!Clust_Judge_Status(clust[id].status))//如果这个簇后面还有文件 就继续读取
Filelist_Update(clust[id].status);
else return;
}
void Filelist_Destroy(){
FileCnt = 0;
fi *p;
for(fi *pre = HEAD; pre != NULL; pre= p){
p = pre->next;
free(pre);
}
HEAD = NULL;
}
void Filelist_Add_File(fi *p){
p->next = HEAD;//直接在头部添加上新结点
HEAD = p;
FileCnt++;
}
int Clust_Judge_Status(int t){
if(t >= 0x2 && t <= 0xFFEF) return 0;//还有连接的簇
else if(t == 0xFFFF) return 1;//文件结束
else return 2;//空簇
}
bool Str_Read_32Bytes(char *str, fi *a){//done
Str_Scanf_String(str, 8, a->name[0]);
Str_Scanf_String(str + 8, 3, a->name[1]);
//这下面吧0xE5改为了-27 (ascii码相同)
if(a->name[0][0] == -27 || a->name[0][0] == 0){//如果该文件已经被删除或者不存在
fseek(fp, 21, SEEK_CUR);//直接跳过剩下32 - 11 = 21个字节
return FALSE;
}
str = str + 11;
if(*str++ == 0x10) //该文件是个目录
a->dir = TRUE;
else a->dir = FALSE;
str += 10;//跳过10个无意义字节
a->time = Str_Scanf_Number(str, 2);//读取时间
str += 2;
a->date = Str_Scanf_Number(str, 2);//读取日期
str += 2;
a->clust = Str_Scanf_Number(str, 2);//读取首簇号
str += 2;
a->len = Str_Scanf_Number(str, 4);//读取文件大小
str += 4;
return TRUE;
}
void File_Printf_32Bytes(fi *t){
File_Printf_String(t->name[0], 8);
File_Printf_String(t->name[1], 3);
if(t->dir == TRUE)
fprintf(fp, "%c", 0x10);
else
fprintf(fp, "%c", 0x20);
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
fprintf(fp, "%c", 0xFF);
File_Printf_Number(t->time, 2);
File_Printf_Number(t->date, 2);
File_Printf_Number(t->clust, 2);
File_Printf_Number(t->len, 4);
}
void Str_Printf_32Bytes(char *str, fi *t){
strncpy(str, t->name[0], 8);
str += 8;
strncpy(str, t->name[1], 3);
str += 3;
if(t->dir == TRUE)
*str++ = 0x10;
else
*str++ = 0x20;
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
*str++ = 0xFF;
Str_Printf_Number(str, t->time, 2);
str += 2;
Str_Printf_Number(str, t->date, 2);
str += 2;
Str_Printf_Number(str, t->clust, 2);
str += 2;
Str_Printf_Number(str, t->len, 4);
}
void Str_Cut_Name_Into_Two(char *name, char *a, char *b){
char temp[30];
strcpy(temp, name);
char *t = temp;
if(strcmp(t, "..") == 0 || strcmp(t, ".") == 0)
strcpy(a, temp);
else{
while(*t != 0 && *t != '.') t++;
if(*t == 0) *(t + 1) = 0;
*t = 0;
strcpy(a, temp);
strcpy(b, t + 1);
}
}
void Filelist_Bubble_Sort(){
for(int i = 0; i < FileCnt; i++)
for(fi *p = HEAD; p->next != NULL; p = p->next)
if(strcmp(p->name[0], p->next->name[0]) > 0){
fi _a, _b, *pnx;//交换函数
pnx = p->next;
_a = *p;
_b = *pnx;
*p = _b;
*pnx = _a;
p->next = _a.next;
pnx->next = _b.next;
}
}
void Data_DBR_Print(){//done
fprintf(fp, "%c%c%c",0xEB ,0x3C ,0x90 );
fprintf(fp, "ByMrh929");
File_Printf_Number(BYTES_PER_SECTOR, 2);
File_Printf_Number(SECTORS_PER_CLUST, 1);
File_Printf_Number(RESERVED_SECTORS, 2);//保留扇区数
File_Printf_Number(2, 1);//FAT数量
File_Printf_Number(512, 2);//根目录项数
File_Printf_Number(SECTORS_PER_FAT, 2);
File_Printf_Number(63, 2);
File_Printf_Number(0, 4);
fprintf(fp, "FAT16 ");
for(int i = 1; i <= 475; i++)
fprintf(fp, "%c", 0x99);
File_Printf_Number(43605, 2);
}
void Data_Add_A_File(fi *F, int id, int k){
char *p = clust[id].byte;
p += k * 32;//将指针移动到需要修改的那个文件信息之前
int newclust = 2;
while(clust[newclust].status != 0) newclust++;//寻找一个簇,用来存放文件的信息
clust[newclust].status = 0xFFFF;
memset(clust[newclust].byte, 0, sizeof(clust[newclust].byte));
F->clust = newclust;
Str_Printf_32Bytes(p, F);
}
void Str_Printf_Number(char *str, long long sum, int n){
long long m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
m = sum % 256;
*str++ = m;//输出一位数并且指针后移
sum /= 256;
}
}
long long Str_Scanf_Number(char *str, int n){//done
long long sum = 0;
char t;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
t = *str++; //读取一位并且指针后移
sum += t * (1 << (i * 8));
}
return sum;
}
void File_Printf_Number(long long sum, int n){//done
long long m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
m = sum % 256;
fprintf(fp, "%c", m);
sum /= 256;
}
}
long long File_Scanf_Number(int n){//done
long long sum = 0;
char t;
for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){
fscanf(fp, "%c", &t);
sum += t * (1 << (i * 8));
}
return sum;
}
void Str_Scanf_String(char *str, int t, char *dest){//done
int i = 0;
while(i < t){
if(*(str + i) != ' ' && *(str + i) != 0){
*(dest + i) = *(str + i);
i++;
}else break;
}
*(dest + i) = 0;
}
void File_Printf_String(char *str, int n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
fprintf(fp, "%c", *(str + i));
}
void Time_Print(int t){//done
int h, m, s;
s = (t & 0x1F) * 2;//取后五位
t >>= 5;
m = t & 0x3F;
t >>= 6;
h = t & 0x1F;
printf("%02d:%02d:%02d", h, m, s);
}
void Date_Print(int t){//done
int y, m, d;
d = t & 0x1F;
t >>= 5;
m = t & 0xF;
t >>= 4;
y = (t & 0xFF) + 1980;
printf("%04d/%02d/%02d", y, m, d);
}
int Time_Get(){//done
time_t t;
struct tm *lt;
time (&t);//获取Unix时间戳。
lt = localtime (&t);//转为时间结构。
return (lt->tm_hour * 2048) + (lt->tm_min * 32) + (lt->tm_sec / 2);
}
int Date_Get(){//done
time_t t;
struct tm *lt;
time (&t);//获取Unix时间戳。
lt = localtime (&t);//转为时间结构。
lt->tm_year += 1900;
lt->tm_mon ++;//0代表1月
return (lt->tm_year - 1980) * 512 + (lt->tm_mon * 32) + (lt->tm_mday);
}
void Dir_Change(char *p, bool NEW){
if(NEW == FALSE)
dir_now--;
else
strcpy(dir[++dir_now], p);
}
void Dir_Print(){
printf("\\");
for(int i = 0; i <= dir_now; i++)
printf("%s\\",dir[i]);
}
int Dir_Find_Empty(int id){
for(int i = 0; i < SECTORS_PER_CLUST * BYTES_PER_SECTOR / 32; i++)
if(clust[id].byte[i * 32] == -27 || clust[id].byte[i * 32] == 0)
return i;
return -1;//没找到一个空位
}
void Make_a_New_File(fi *p, bool IsDir){
p->clust = 1;
p->len = 0;
p->dir = IsDir;
p->time = Time_Get();
p->date = Date_Get();
p->name[1][0] = 0;
}
void Clust_Clear_File(int id){
if(Clust_Judge_Status(clust[id].status) == 0)//还有连接的簇
Clust_Clear_File(clust[id].status);
clust[id].status = 0;//标记为未使用
return;
}
void Clust_Clear_Dir(int id){
//先搜索这个文件夹下有哪些子文件和目录,把它们删除,然后再删除自身
if(id <= 0) return;
fi t;
for(int i = 2; i < SECTORS_PER_CLUST * BYTES_PER_SECTOR / 32; i++)
if(Str_Read_32Bytes(clust[id].byte + 32 * i, &t)){//如果读取成功,就申请一段新内存来存文件
if(t.dir == TRUE)
Clust_Clear_Dir(t.clust);//递归删除子目录
else
Clust_Clear_File(t.clust);//递归删除子文件
*(clust[id].byte + 32 * i) = 0xE5;//标记为删除
}
if(Clust_Judge_Status(clust[id].status) == 0)//如果这个簇后面还有文件 就继续读取
Clust_Clear_Dir(clust[id].status);
}
void Manu_Print(){//done
printf("This system supports the following commands:\n\n");
printf("ls/dir\t\t\t\t\tShow the files and folders contained.\n");
printf("cd [DIR]\t\t\t\tEnter an appinted folder.\n");
printf("mkdir [DIR]\t\t\t\tCreate a folder.\n");
printf("create [NAME]\t\t\t\tCreate a file.\n");
printf("rmdir [DIR]\t\t\t\tDelete a folder.\n");
printf("rm [NAME]\t\t\t\tDelete a file.\n");
printf("read [NAME]\t\t\t\tRead a file.\n");
printf("write [NAME]\t\t\t\tWrite a file.\n");
printf("format\t\t\t\t\tFormat this disk.(be careful)\n");
printf("save\t\t\t\t\tSave this disk and quit.(without which you'll lose your data)\n\n\n");
}





Comments | NOTHING